易
經
Yi Jing 
 – I Ching, the Book of Changes
– I Ching, the Book of Changes
This famous system of 64 hexagrams plus their commentaries and transformations is at the root of Chinese thought. Tr. Wilhelm (en, fr).
| 17. 隨 Sui / Following | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
current binomial swap trig. opposite flip X leading master X constituent master
The Hexagram
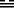

Above TUI THE JOYOUS, LAKE
Below CHÊN THE AROUSING, THUNDER
The trigram Tui, the Joyous, whose attribute is gladness, is above; Chên, the Arousing, which has the attribute of movement, is below. Joy in movement induces following. The Joyous is the youngest daughter, while the Arousing is the eldest son. An older man defers to a young girl and shows her consideration. By this he moves her to follow him.
The Judgment

Perseverance furthers. No blame.
In order to obtain a following one must first know how to adapt oneself. If a man would rule he must first learn to serve, for only in this way does he secure from those below him the joyous assent that is necessary if they are to follow him. If he has to obtain a following by force or cunning, by conspiracy or by creating factions, he invariably arouses resistance, which obstructs willing adherence. But even joyous movement can lead to evil consequences, hence the added stipulation, "Perseverance furthers"–that is, consistency in doing right–together with "No blame. " Just as we should not ask others to follow us unless this condition is fulfilled, so it is only under this condition that we can in turn follow others without coming to harm.
The thought of obtaining a following through adaptation to the demands of the time is a great and significant idea; this is why the appended judgment is so favorable.
The Image

The image of FOLLOWING.
Thus the superior man at nightfall
Goes indoors for rest and recuperation.
In the autumn electricity withdraws into the earth again and rests. Here it is the thunder in the middle of the lake that serves as the image–thunder in its winter rest, not thunder in motion. The idea of following in the sense of adaptation to the demands of the time grows out of this image. Thunder in the middle of the lake indicates times of darkness and rest. Similarly, a superior man, after being tirelessly active all day, allows himself rest and recuperation at night. No situation can become favorable until one is able to adapt to it and does not wear himself out with mistaken resistance.
Lower line

The standard is changing.
Perseverance brings good fortune.
To go out of the door in company
Produces deeds.
There are exceptional conditions in which the relation between leader and followers changes. It is implicit in the idea of following and adaptation that if one wants to lead others, one must remain accessible and responsive to the views of those under him. At the same time, however, he must have firm principles, so that he does not vacillate where there is only a question of current opinion. Once we are ready to listen to the opinions of others, we must not associate exclusively with people who share our views or with members of our own party; instead, we must go out and mingle freely with all sorts of people, friends or foes. That is the only way to achieve something.
Second line

If one clings to the little boy,
One loses the strong man.
In friendships and close relationships an individual must make a careful choice. He surrounds himself either with good or with bad company; he cannot have both at once. If he throws himself away on unworthy friends he loses connection with people of intellectual power who could further him in the good.
Third line

If one clings to the strong man,
One loses the little boy.
Through following one finds what one seeks.
It furthers one to remain persevering.
When the right connection with distinguished people has been found, a certain loss naturally ensues. A man must part company with the inferior and superficial. But in his heart he will feel satisfied, because he seeks and needs for the development of his personality. The important thing is to remain firm. He must know what he wants and not be led astray by momentary inclinations.
Fourth line

Following creates success.
Perseverance brings misfortune.
To go one's way with sincerity brings clarity.
How could there be blame in this?
It often happens, when a man exerts a certain amount of influence, that he obtains a following by condescension toward inferiors. But the people who attach themselves to him are not honest in their intentions. They seek personal advantage and try to make themselves indispensable through flattery and subservience. If one becomes accustomed to such satellites and cannot do without them, it brings misfortune. Only when a man is completely free from his ego, and intent, by conviction, upon what is right and essential, does he acquire the clarity that enables him to see through such people, and become free of blame.
Fifth line
Upper line

He meets with firm allegiance
And is still further bound.
The king introduces him
To the Western Mountain.
This refers to a man, an exalted sage, who has already put the turmoil of the world behind him. But a follower appears who understands him and is not to be put off. So the sage comes back into the world and aids the other in his work. Thus there develops an eternal tie between the two.
The allegory is chosen from the annals of the Chou dynasty. The rulers of this dynasty honored men who had served them well by awarding them a place in the royal family's temple of ancestors on the Western Mountain. In this way they were regarded as sharing in the destiny of the ruling family.
axcelmunchen

I Ching, the Book of Changes – Yi Jing I. 17. – Chinese on/off – Français/English
Alias Yijing, I Ching, Yi King, I Ging, Zhou yi, The Classic of Changes (Lynn), The Elemental Changes (Nylan), Le Livre des Changements (Javary), Das Buch der Wandlung.
The Book of Odes, The Analects, Great Learning, Doctrine of the Mean, Three-characters book, The Book of Changes, The Way and its Power, 300 Tang Poems, The Art of War, Thirty-Six Strategies
Welcome, help, notes, introduction, table.
Index – Contact – Top